What Is The Makeup Of Bronze

Along with copper, bronze and brass belong to a category of metals referred to every bit "red metals" due to their distinct cherry color. These 2 materials are copper-based alloys containing varying amounts of other elements that produce a wide range of different properties.
For instance, bronze typically consists of copper and tin can, but other elements may likewise characteristic in the composition. Regardless of the elemental improver, bronze demonstrates greater hardness than pure copper. On the other manus, brass mainly contains copper and zinc, the latter of which allows for enhanced strength and ductility.
Although there are similarities between brass and bronze, the post-obit mail service focuses on the individual characteristics, properties, and benefits of each material and the differences between them.
What Is Statuary?
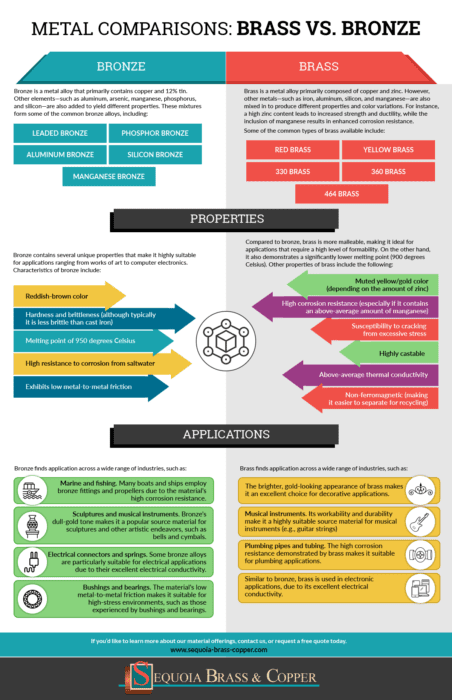
Bronze is a metal alloy that primarily contains copper and 12% tin can. Other elements—such as aluminum, arsenic, manganese, phosphorus, and silicon—are too added to yield different properties. These mixtures class some of the common bronze alloys, including:
- Leaded bronze
- Phosphor bronze
- Aluminum bronze
- Silicon statuary
- Manganese statuary
Properties of Bronze
Statuary contains several unique properties that brand it highly suitable for applications ranging from works of fine art to computer electronics. Characteristics of statuary include:
- Reddish-brown color
- Hardness and brittleness (although typically it is less brittle than cast iron)
- Melting point of 950 degrees Celsius
- High resistance to corrosion from saltwater
- Exhibits depression metal-to-metal friction
Applications of Bronze
Bronze'south characteristics make information technology suitable for utilise in functional and aesthetic applications, such every bit:
- Marine and fishing. Many boats and ships utilize statuary fittings and propellers due to the textile'southward high corrosion resistance.
- Sculptures and musical instruments. Bronze's dull-gold tone makes it a popular source material for sculptures and other creative endeavors, such equally bells and cymbals.
- Electrical connectors and springs. Some bronze alloys are particularly suitable for electrical applications due to their excellent electrical electrical conductivity.
- Bushings and bearings. The material's low metal-to-metal friction makes information technology suitable for high-stress environments, such as those experienced by bushings and bearings.
What Is Brass?
Brass is a metal alloy primarily equanimous of copper and zinc. All the same, other metals—such as iron, aluminum, silicon, and manganese—are also mixed in to produce different properties and color variations. For example, a loftier zinc content leads to increased strength and ductility, while the inclusion of manganese results in enhanced corrosion resistance.
Some of the common types of brass bachelor include:
- Red contumely
- Xanthous brass
- 330 brass
- 360 brass
- 464 brass
Properties of Brass
Compared to bronze, brass is more malleable, making it ideal for applications that crave a high level of formability. On the other hand, it likewise demonstrates a significantly lower melting bespeak (900 degrees Celsius).
Other properties of brass include the following:
- Muted xanthous/gold colour (depending on the amount of zinc)
- Loftier corrosion resistance (particularly if it contains an above-boilerplate amount of manganese)
- Susceptibility to cracking from excessive stress
- Highly castable
- Above-average thermal conductivity
- Non-ferromagnetic (making it easier to dissever for recycling)
Applications of Brass
Brass finds application across a wide range of industries, such as:
- The brighter, gilt-looking advent of contumely makes information technology an excellent option for decorative applications.
- Musical instruments. Its workability and durability go far a highly suitable source textile for musical instruments (e.g., guitar strings)
- Plumbing pipes and tubing. The high corrosion resistance demonstrated by brass makes it suitable for plumbing applications.
- Similar to bronze, contumely is used in electronic applications, due to its first-class electrical conductivity.
The Differences Betwixt Bronze and Brass
The differences in material compositions between bronze and contumely result in varying characteristics that brand them suitable for different use cases. For instance, bronze'southward college level of resistance to saltwater corrosion makes it a improve option for ship components than contumely, while brass'due south exceptional workability and machinability make it more suitable for tubing and pole applications. Tabular array 1 below outlines some of the major differences betwixt the two materials.
Tabular array 1 – Differences Betwixt Bronze and Brass
| Bronze | Contumely |
| Harder, more than brittle | Greater malleability |
| Melting indicate of 950 degrees Celsius | Melting indicate of 900 degrees Celsius |
| Excellent corrosion resistance (incl. saltwater) | Good corrosion resistance |
| Suitable for some decorative applications (east.chiliad., sculptures, musical instruments, etc.) | More suited for decorative applications (due to gold color) |
| Dates back to 3500 BCE | Dates back to 500 BCE |
Contact Sequoia Brass & Copper Today
Contumely and bronze are ii copper-based alloys that offer a multifariousness of characteristics suitable for a wide range of applications. At Sequoia Contumely & Copper, nosotros offering an extensive selection of bronze and brass materials in bar, plate, tube, rod and canvas class to suit your unique awarding. If you'd like to larn more almost our material offerings, contact usa, or asking a free quote today.
Source: https://www.sequoia-brass-copper.com/blog/brass-vs-bronze/
Posted by: lujanthicents.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Makeup Of Bronze"
Post a Comment